Science Behind Skin Growth Healing
Article from Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology — Skin rejuvenation using cosmetic products Review of the literature
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5108505/#
Abstract
Skin aging is primarily due to alterations in the dermal extracellular matrix, especially a decrease in collagen I content, fragmentation of collagen fibrils, and accumulation of amorphous elastin material, also known as elastosis. Growth factors and cytokines are included in several cosmetic products intended for skin rejuvenation because of their ability to promote collagen synthesis. Matrikines and matrikine-like peptides offer the advantage of growth factor-like activities but better skin penetration due to their much smaller molecular size. In this review, we summarize the commercially available products containing growth factors, cytokines, and matrikines for which there is evidence that they promote skin rejuvenation.
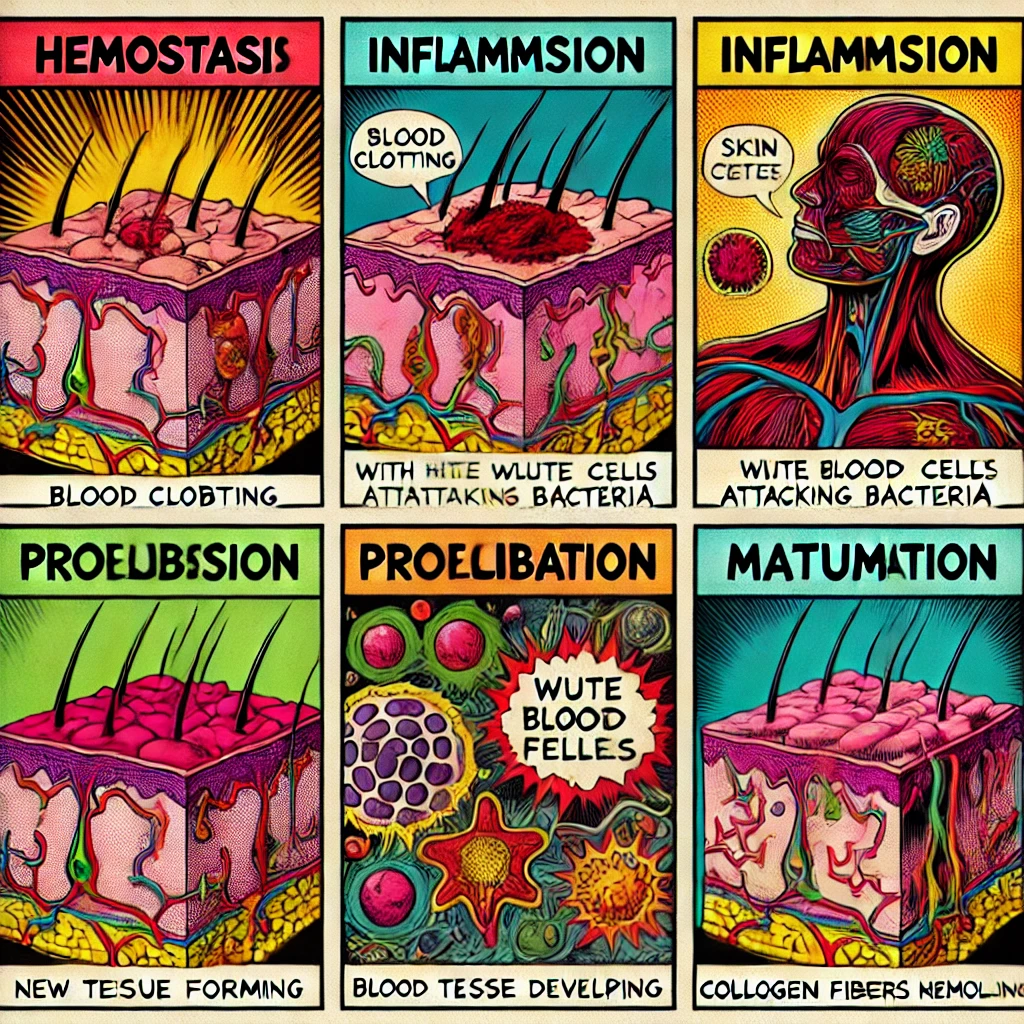
Skin growth and healing are complex processes that involve a series of coordinated cellular and molecular events to restore the skin’s integrity after injury. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing effective treatments and cosmetic products aimed at enhancing skin rejuvenation.
Phases of Wound Healing
Wound healing typically progresses through several overlapping stages:
- Hemostasis: Immediately after injury, blood vessels constrict, and clotting mechanisms are activated to prevent blood loss.
- Inflammation: White blood cells, including macrophages, arrive at the injury site to eliminate bacteria and debris, setting the stage for tissue repair.
- Proliferation: This phase involves the formation of granulation tissue, angiogenesis (development of new blood vessels), collagen deposition, and re-epithelialization, where new skin cells cover the wound.
- Maturation (Remodeling): The final phase involves the remodeling of collagen fibers, increasing the tensile strength of the new tissue.
Role of Growth Factors and Cytokines
Growth factors and cytokines are pivotal in regulating the wound healing process. They promote cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. For instance, Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) stimulates keratinocyte and fibroblast proliferation, enhancing tissue regeneration. As we age, the levels of these growth factors decrease, leading to diminished skin repair capabilities. Topical application of EGF has been shown to signal for healing, cellular division, and increased protein synthesis, thereby promoting skin health.
Matrikines and Matrikine-like Peptides
Matrikines are peptide fragments derived from the extracellular matrix (ECM) that regulate cell activity. They mimic the activity of growth factors but have better skin penetration due to their smaller size. Incorporating matrikines into cosmetic products can promote collagen synthesis, aiding in skin rejuvenation.
Advancements in Wound Healing Therapies
Recent research has explored innovative approaund healing:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Utilizing stem cells to promote tissue regeneration has shown promise in improving wound healing outcomes.
- Nanotherapeutics: Nanoparticles can deliver therapeutic agents directly to the wound site, enhancing healing efficiency.
- 3D Bioprinting: This technology allows for the creation of customized skin grafts that can be applied to extensive wounds, promoting better integration and healing.
Impact of Aging on Skin Healing
Aging leads to alterations in the dermal extracellular matrix, such as a decrease in collagen content and fragmentation of collagen fibrils. These changes result in reduced skin elasticity and slower wound healing. Cosmetic products containing growth factors, cytokines, and matrikines aim to counteract these effects by promoting collagen synthesis and enhancing skin rejuvenation.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind skin growth and healing has paved the way for advanced therapeutic and cosmetic interventions. Incorporating growth factors, cytokines, and matrikines into skincare products offers promising avenues for enhancing skin rejuvenation and repair, particularly in aging populations. Ongoing research continues to explore innovative methods to optimize wound healing and restore skinvely.