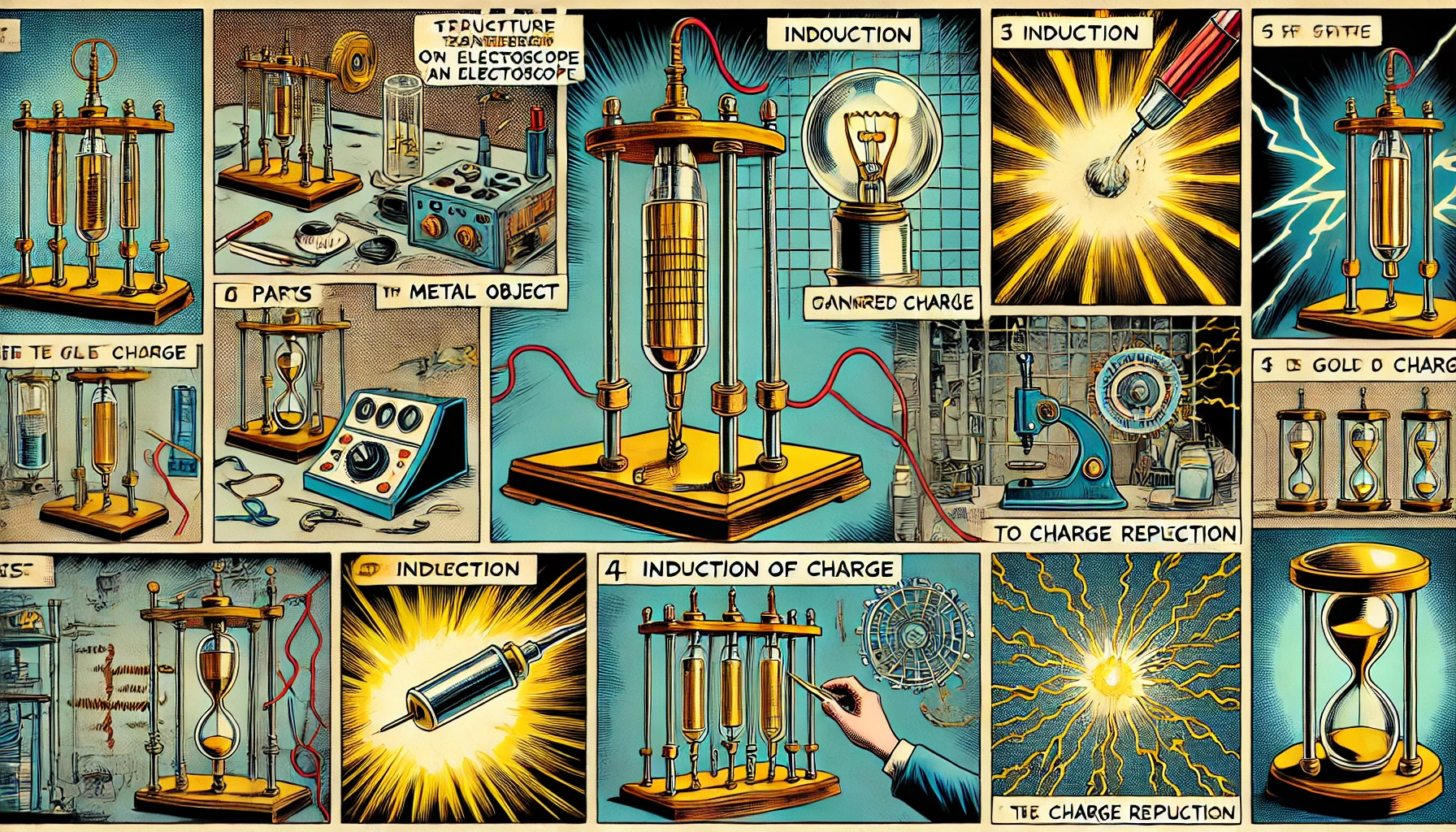
Why Gold Leaf used in Electroscope
Gold leaf is used in electroscopes due to its unique physical properties and the critical role it plays in detecting electric charge. Here’s why it is specifically chosen:
1. High Sensitivity to Charge
Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity. When an electroscope is charged, the gold leaf quickly responds to the introduction of an electric charge by repelling or attracting other conductive parts in the device. This sensitivity makes it ideal for detecting even very small amounts of electric charge.
2. Flexibility and Thinness
Gold leaf is extremely thin (measured in microns), making it lightweight and highly responsive to electrostatic forces. Its low mass allows it to move easily in response to small forces, enhancing the sensitivity of the electroscope.
3. Malleability
Gold is one of the most malleable materials, meaning it can be hammered into very thin sheets without breaking. This allows the gold leaf to be extremely delicate yet durable enough to function in a precision instrument like an electroscope.
4. Resistance to Corrosion
Gold is highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. Unlike other metals, it does not tarnish when exposed to air or moisture. This ensures the gold leaf remains functional and sensitive over long periods without degrading or requiring replacement.
5. Visible Movement
The movement of the gold leaf is easy to observe, even under minimal charge influence. This makes it an excellent indicator in a scientific instrument where detecting and measuring charge is the primary goal.
Function in an Electroscope
- Neutral State: When there is no charge, the gold leaf hangs straight down.
- Charged State: When a charge is introduced to the electroscope, the gold leaf repels from the conducting rod (due to like charges repelling) or moves toward it (if opposite charges are present).
- Measurement: The degree of deflection indicates the amount of charge present, with more charge causing greater movement.
Understanding the Electroscope
An electroscope is a simple device used to detect and measure electric charge. It is one of the earliest tools used in electrostatics and serves as the foundation for understanding modern electrical phenomena.
Components of an Electroscope
- Metal Rod:
- A conductive rod that transfers charge to the gold leaf.
- It is often connected to a terminal or knob at the top for introducing charge.
- Gold Leaf:
- A thin, lightweight piece of gold leaf attached to the bottom of the rod.
- This component reacts to the presence of electric charge.
- Support Frame:
- Insulates the rod from external influences and holds it in place.
- Often made of a non-conductive material like glass or plastic to prevent charge leakage.
- Glass Case:
- Encases the gold leaf and rod to protect them from airflow and moisture.
- Ensures accurate readings by reducing environmental interference.
How an Electroscope Works
The electroscope operates on the principles of electrostatic induction and charge repulsion.
Step 1: Charging by Contact
- When a charged object touches the metal terminal, the charge is transferred to the gold leaf via the rod.
- If the object is positively charged, electrons flow from the electroscope to the object, leaving the electroscope positively charged, and vice versa.
Step 2: Charging by Induction
- When a charged object is brought near (but does not touch) the terminal, it induces a charge separation within the electroscope.
- Opposite charges are attracted to the terminal, and like charges repel to the gold leaf, causing it to move.
Step 3: Gold Leaf Reaction
- The gold leaf deflects from the rod because like charges repel.
- The degree of deflection corresponds to the magnitude of the charge.
Applications of the Electroscope
- Detecting Charge:
- An electroscope can determine if an object is charged by observing the gold leaf’s movement.
- Type of Charge:
- Using induction and known charges, the type of charge (positive or negative) on an object can be inferred.
- Measuring Charge:
- Although basic electroscopes are qualitative, advanced versions like the gold-leaf electroscope can give rough estimates of charge magnitude.
- Detecting Radiation:
- Electroscopes can detect ionizing radiation by observing how quickly the gold leaf collapses (radiation ionizes air, allowing charge to dissipate).
- Educational Tool:
- Used in teaching fundamental concepts of electrostatics and charge interaction.
Limitations
- Low Sensitivity to Small Charges:
- Modern instruments like electrometers are more precise.
- Environmental Factors:
- Humidity can interfere with the electroscope’s function as it allows charge leakage through air.
- Qualitative Nature:
- Standard electroscopes are not capable of precise charge measurement.
Modern Relevance
While largely replaced by electronic instruments, electroscopes remain important for:
- Demonstrations in physics education.
- Use in environments without access to advanced technology.
Here are some informative videos demonstrating the use of gold leaf in electroscopes:
- Gold Leaf Electroscope: This video explains the working of a gold leaf electroscope through simple animations, making it easy to understand for students.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kc85v2mCn5U - How an Electroscope Works | Gold Leaf Electroscope 3D Animation: This detailed 3D animation illustrates how an electroscope functions, highlighting the principles behind this charge detection instrument.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QwGvQDCt_us - Using a Gold-Leaf Electroscope with Zinc Plate and Ultraviolet Light: Produced by the Institute of Physics, this video demonstrates how to use a gold-leaf electroscope in conjunction with a zinc plate and ultraviolet light source.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OUAplNaGD-c - How Does a Gold Leaf Electroscope Work: This video provides a simple yet effective explanation of the gold leaf electroscope, detailing its components and functionality.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3kTFwmMTOkI - Gold Leaf Electroscope: This educational video offers an overview of the gold leaf electroscope, including its construction and operation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iu6QCvQCkMc
These resources should provide a comprehensive understanding of how gold leaf is utilized in electroscopes.